IT House News, May 10
Recently, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued wireless radio frequency licenses and space radio station licenses to Tsinghua University for the Smart Sky Network 01 satellite, supporting Tsinghua University’s exploration of mid-orbit wideband synchronous orbit communication satellite technology verification.
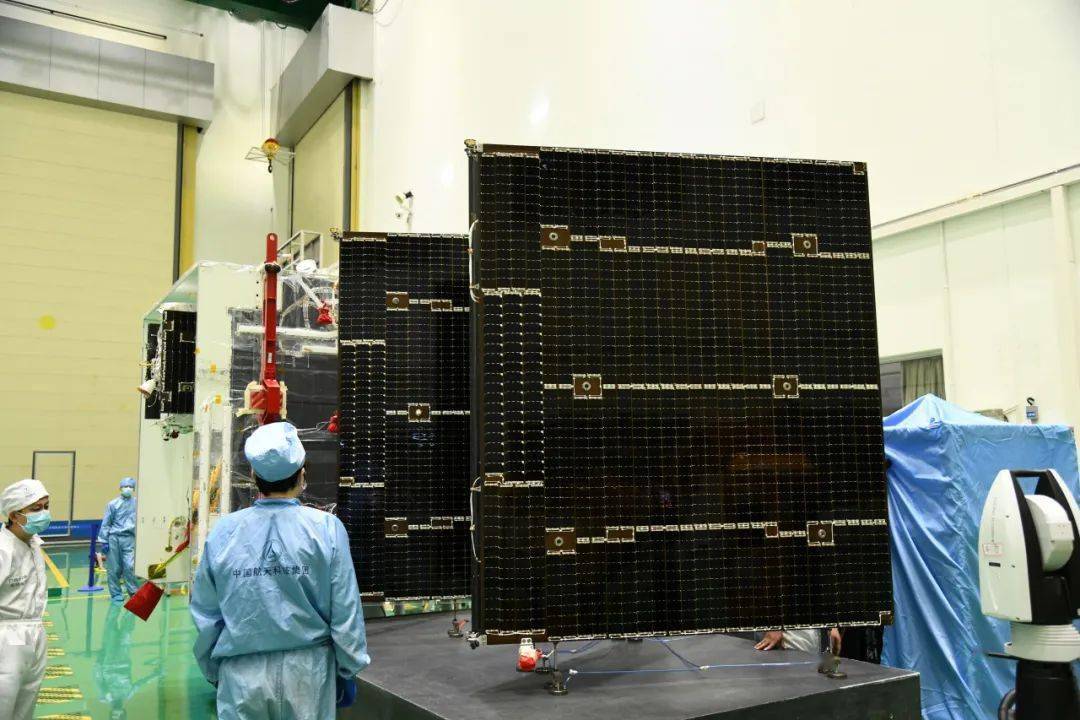

▲ Smart Sky Network 01 Satellite, Image Source: Shanghai Aerospace Technology Research Institute
The Smart Sky Network 01 satellite is China’s first mid-orbit wideband communication test satellite. Its use of radio frequencies involves multiple bands. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has completed the coordination of relevant frequencies according to regulations and issued licenses accordingly, providing wireless radio frequency resources support for Tsinghua University’s research data direct connection between domestic and Antarctic scientific research stations, and for the verification of various new technologies such as mid-orbit and high-low orbit satellite data transmission.
Next, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology will focus on satellite industry and technology development, guiding relevant satellite operating units to use satellite radio frequencies reasonably, conduct frequency coordination in an orderly manner, and ensure the demand for frequency use in space-based networks.
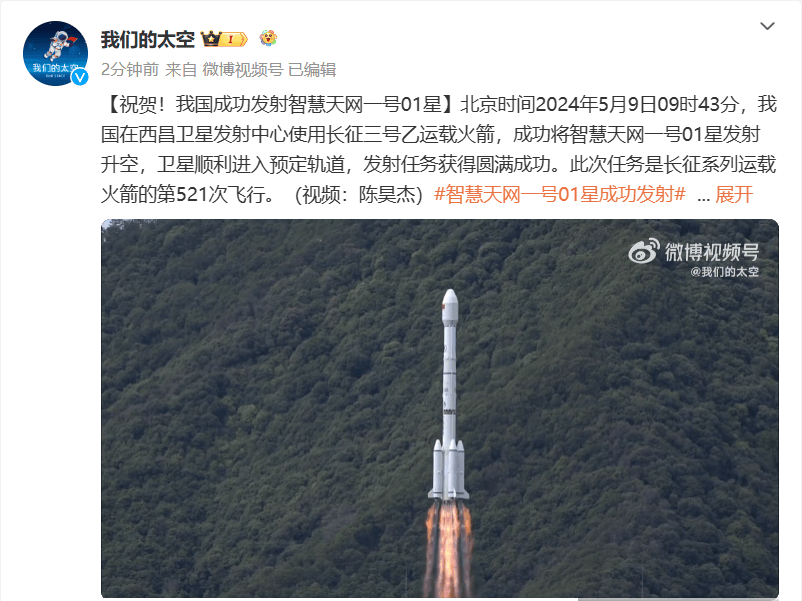
According to previous reports by IT House, on May 9, 2024, at 9:43 a.m., the Long March 3B carrier rocket successfully lifted off from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center, sending the Smart Sky Network 01 satellite (A/B) into the designated orbit, achieving a complete success in the launch mission.
“Smart Sky Network” is a mid-orbit wideband synchronous orbit space network solution proposed by Tsinghua University. It consists of 8 mid-orbit broadband communication network satellites deployed in a 20,000-kilometer orbit, forming a globally covered communication constellation. It can be expanded on demand to 16 satellites (two groups), 32 satellites (four groups), and other multi-coverage networks.
Once the constellation is completed, it will achieve personalized broadband network services with global non-blind spot coverage. It can also collaborate with low-orbit satellite internet and high-orbit satellite internet to build a unified space-to-ground 6G network, realizing access for various users in all scenarios and domains.